With the increase in the numbers of Electric Vehicles, there is a need for more fuel to run them, and fuel to the EVs is the Electric Charge, which the Electric Vehicle Charging Stations supply. But have you ever thought that how the charging station works and fully charge the battery of your car in a half-hour? Let’s look at the basic structure and the working of the Charging stations under the title How EV Charging Stations Work?
☛ What You will Read here
What is a Charging Station?
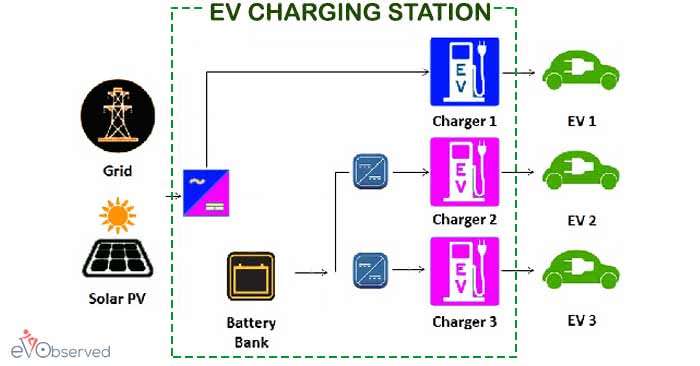
A charging station or Electric Recharge point is a junction where multiple Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment(EVSE) or Car Chargers are installed which offers fast charging options to multiple vehicles such as Electric Scooters, Electric Cars, Hybrid Vehicles, etc. at a time.
What is there that needs to be charged?
Electric vehicles are packed with high-capacity Lithium-Ion(Li-Ion) batteries which need to be charged when the charge level drops below a certain limit. The charged battery provides the charge(fuel for Electric Vehicle) to the motor which in return produces high torque and makes the vehicle move.
Recommended: 4 Types of Electric Vehicles : Know the Difference Here!
Structure of a Charging Station?

In the earlier times, charging stations used to have pre-charged battery packs kept with them, which were used to get replaced by your discharged battery for a fixed price. The discharged batteries were then made fit for reuse by recharging. With the improvement in the design of cars which made the batteries non-removable, the charging stations also evolved by providing a battery charging option instead of a battery replacement. The battery Charging station has particular components:
Sufficient Parking Place
A Charging station has a sufficient parking space that can park the vehicles while charging for a longer time. Since a charger can charge multiple EVs at a time so sufficient parking space is necessary.
Input Power Supply
To understand How EV Charging Stations Work we need to understand the input power supply first. Since the charging stations also need a source of power supply to maintain a continuous supply of required power output. The input to the charging station is AC which is converted to DC with the help of a rectifier for charging purposes.
Some charging stations also have solar panels installed on their roof head which offer cheaper charging rates at the peak time(when solar energy delivered by the sun is maximum) of the day. Tesla has solar panels installed on the roofs of their charging stations.
Charger
The charger is the main component of an EV charging station which supplies energy to the vehicle. The chargers have HMI(Human Machine Interface) like TouchScreens embedded in them which lets users regulate the Charging Time, percentage of charge, payment, etc. Chargers have different pins such as:
- Control Pilot: Chargers have a control circuit that delivers control signals to the car through the Control Pilot pin. It regulates the flow of current required within the safe limits and transmits the essential data for efficient charging. The Control circuit sends PWM(Pulse Width Modulated) signal to the car to make sure that the car only gets power below the
- Proximity Pilot: Apart from Control Pilot, the charger has a Proximity Pilot Port which is used to ensure the proper connection between the EV and the charger. If the connection is not propper then due to the signal passed through Proximity Pilot, the charging will stop.
Also Check: Are Cities Ready For E-bikes? Major problems and Progress
Charging connectors

All the chargers have the same basic configuration, but the difference lies in the power supplied and the design of the Charging connectors. Different types of connectors vary according to the Manufacturer, Region, Charging Time, Power Output, and cost. After power supply connecter is an important part to understand. So, under the title How EV Charging Stations Work we are also providing details of types of power and connectors depending on it. There are two types of Powers and depending upon which, there are different connectors:
Alternating Current (AC)
AC or the alternating current offers sinusoidal power to the vehicle which is then converted to the DC with the help of an onboard circuit or the circuit employed within the charger. Depending upon the different power parameters such as Voltage and Frequency in different regions, AC charging connectors are of the following types:
- Type 1 Connector: SAE J1772 or the Type 1 connector is the most commonly used in Asia and the US. It is a single-phase AC connector having two AC supply Pins, One earth, and 2 Signal Pins. Type 1 connector can handle a maximum of 80A current at a maximum voltage of 120 V or 240 V.
- Type 2 Connector: SAE J3068 Commonly referred to as Type 2 or Mennekes connector offers Single-phase charging with 80 A maximum current rating at 230 V and Three-phase charging at 63 A current rating at 400V. These are most common in Europe where high voltage supply is available. These circular-shaped connectors with a flat top edge have 7 pins(3 for Different phases, 1 pin for neutral, 1 pin for grounding, 1 for Control Pilot, and 1 for Proximity Pilot). NOTE: Tesla uses a Type 2 Connector in Europe.
- Type 3 Connector: SC23H or the EV Alliance Type 3 connectors are also used in Europe, but there are now replaced by the type 2 connectors mostly. It is also available in 3 phase and single-phase variants and mostly has protective caps for protection from Electrocution.
Direct Current (DC)
DC or the Direct Current is the most used type to charge the battery because it offers fast charging. These CCS connectors can carry current up to 350 A within the voltage range of 200-1000V and can deliver power up to 350kW. Like AC, it also has a different type of Connectors as:
- CCS(Combined Charging System): CCS is the combined charging connector that has both the AC and DC Pins for charging. CCS have two types of Connectors:
- Combo 1: Combo 1 is derived from the Type 1 AC Connector as it has 2 DC pins in addition to the Type 1 AC connector.
- Combo 2: It is derived from the Type 2 AC connector which supports both AC and DC charging. In addition to the type 2 AC connector design, it has 2 extra DC pins for DC charging.
- CHAdeMO: CHAdeMO stands for “CHArge de MOve” which means “move using charge” or “move by charge” to indicate that it is a fast charger. CHAdeMO has a total of 9 Pins from which 3(1 for Ground and 2 for DC input) are the Charging Pins while the other 6 Pins are the signal pins for Charge Start/Stop, Charge Enable/Disable, CAN-H, CAN-L, and Proximity Control functions. Here CAN stands for Control Area Network which allows Microcontrollers and different devices to communicate with each other in real-time without the need of a Host Computer. CHAdeMO offers two versions:
- Version 1.2 can carry current up to 400A within the voltage range of 50-500V and deliver power up to 200 kW.
- Version 2.0 can carry 400A current within a voltage range up to 1000 V and can carry a power of 400 kW.
Tesla Charger
For the US, TESLA has made a standard 5 Pin connector that supports both the AC and DC charging over the same design. Tesla Supercharger is the fastest charger that can charge up to 150 kW. For Europe, Tesla uses Type 2 chargers.
Also Read: Tesla Model 3 : What is new in 2021 Model?
How do EV charging stations work?

So, after shedding light on each and every part of the EV Charging Station let’s take a look at How do EV Charging Stations Work. Charging works slightly differently in both AC and DC to the different circuitry. It can be understood as:
DC Charging
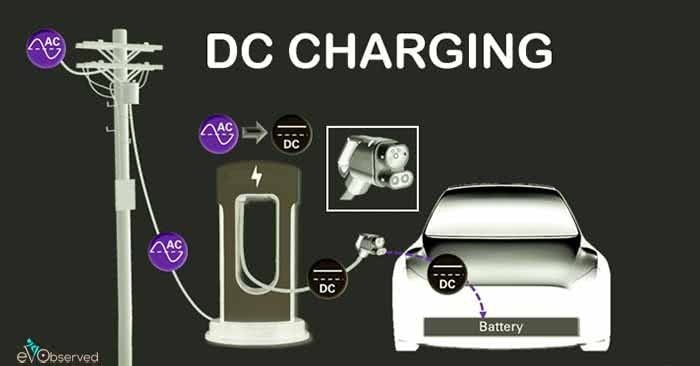
The AC power supplied by the AC grid is converted into DC with the help of a rectifier. Then the Power Control Unit delivers the controlled Voltage and Current to charge the battery. The Protection circuit ensures the safety of equipment and the users. The Battery Management System(BMS) ensures that the battery is optimally charged and also ensures proper communication between the charging station and the battery.
AC Charging
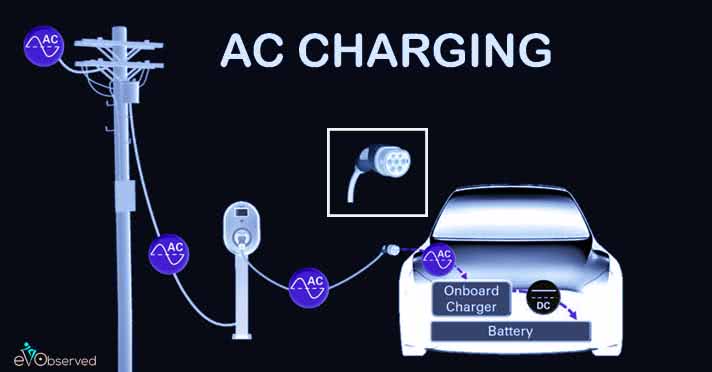
When the Connector is plugged for the first time into EV then the Charge controller of the Charging Station communicates with the on-board charger and exchanges data about the current limits, Faults, Battery Percentage, etc. After that, the Charging station starts supplying AC power to the Charger which converts it into the DC with the help of a Rectifier while the power control circuit controls the Current and Voltage parameters and supplies power to the battery for charging purposes. Like DC charging there is also a Protection circuit for Protection and a BMS(Battery Management System) to track parameters like Voltage, Current, and Temperature to ensure that the battery charges within safe limits.
How EV Charging Stations Work : AC vs DC charging
AC charging is the earlier method that offers slow charging and there are many heating issues for higher power ratings while the DC offers the fastest charging without heating issues. AC charging beats DC charging only in case of expenses because affording an AC charger is much economical than buying a DC charger. CHAdeMO is the fastest DC charging technology that can charge EVs in less than an hour.
Battery charging Providers
There are different third-party battery charging providers around America such as Electrify America, IONITY(Joint venture of Ford, BMW, Audi, Mercedes, Volkswagen, and Porsche), etc. Tesla has its network of thousands of charging stations with fast charging Superchargers installed around America.
NOTE: Nowadays, Charging stations have different connectors for different types of EVs. You can confirm the connector type of EV from the Manufacturer or can visually match the connector and the EV’s charging socket.
For better and efficient On-the-go charging, DC is the best option while AC serves best for homes.
How EV Charging Stations Work : Conclusion
There are various charging stations that feature most of the types of EV Charging points at a single place similar to what we see at the Petrol pump or fuel stations. A major problem with Electric vehicles is that they still don’t feature uniform connectors, however, the EV industry is moving toward that too. But this article will be enough to provide details of how do EV Charging works? and many more cool details.
That’s it under the How EV Charging Stations Work topic, we will keep it updated and also trying to add more details. check our other topics and enjoy the knowledge EV Observed is providing. Please do follow our social pages and subscribe to our newsletter. Keep visiting our EV Blog Thank You and have a great day.






